SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES DECIDES KAPPOS v. HYATT
[April 18, 2012]
JUSTICE THOMAS delivered the opinion of the Court.
Under the Patent Act of 1952, if a Patent and Trade Office (PTO) examiner denies a patent application, 35 U. S. C. §131, the applicant may file an administrative appeal with the PTO’s Board of Patent Appeals and Interferences, §134. If the Board also denies the application, the applicant may appeal directly to the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit under §141. Alternatively, the applicant may file a civil action against the PTO Director under , which permits the applicant to present evidence that was not presented to the PTO.
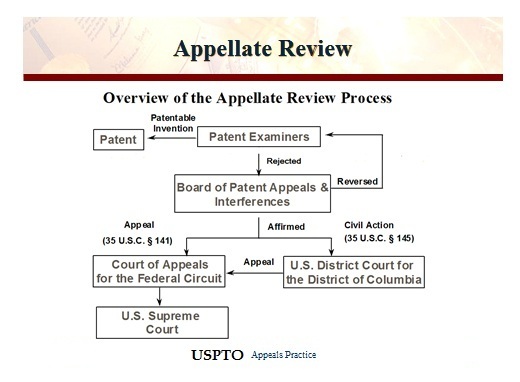
Respondent Hyatt filed a patent application covering multiple claims. The patent examiner denied all of the claims for lack of an adequate written description. Hyatt appealed to the Board, which approved some claims but denied others. Pursuant to §145, Hyatt filed a civil action against the Director, but the District Court declined to consider Hyatt’s newly proffered written declaration in support of the adequacy of his description, thus limiting its review to the administrative record. Applying the deferential “substantial evidence” standard of the Administrative Procedure Act (APA) to thePTO’s factual findings, the court granted summary judgment to the Director. On appeal, the Federal Circuit vacated the judgment, holding that patent applicants can introduce new evidence in §145 proceedings, subject only to the limitations in the Federal Rules of Evidence and the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure. It also reaffirmed its precedent that when new, conflicting evidence is introduced, the district court must make de novo findings to take such evidence into account.
